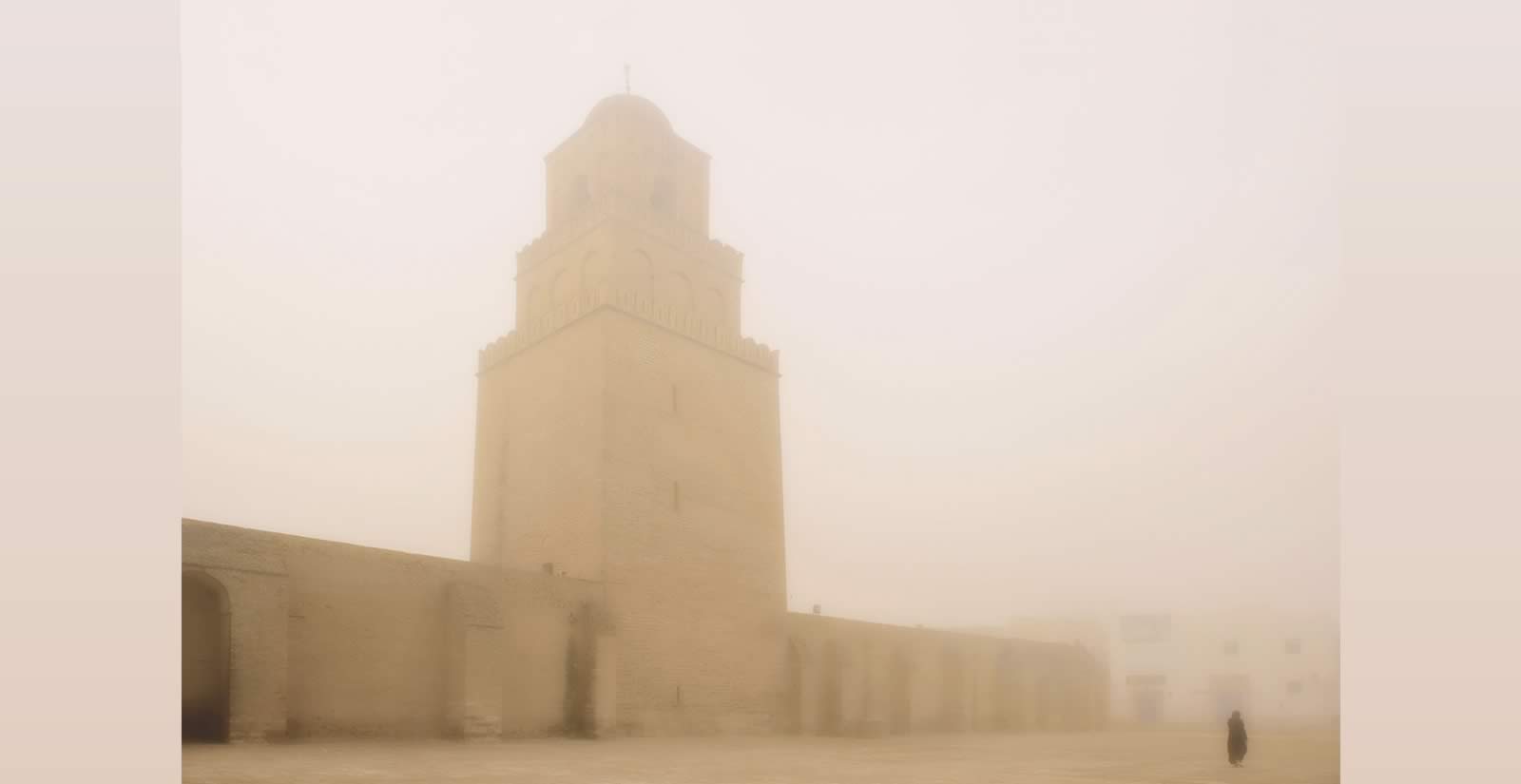
Africa's First City of Islam
Founded on a plain between sea and hills in the year 670 CE, Kairouan became a capital of dynastic power and a cultural beacon, the center for the spread of Muslim Arab influence through North Africa and southern Europe— not only in religion, but also in architecture, medicine, education, law and more.
Founded on a plain between sea and hills in the year 670 CE, Kairouan became a capital of dynastic power and a cultural beacon, the center for the spread of Muslim Arab influence through North Africa and southern Europe— not only in religion, but also in architecture, medicine, education, law and more.
In the mid-seventh century, the Arab expansion reached the Mediterranean Sea, which was dominated then by the Byzantine Empire. In much the same way the sea was a field of power for Byzantine fleets, so, too, would the desert become for the Arabs—an alternate, rival realm. From it, their influence would spread across North Africa and southern Europe. Where this started was Kairouan. Now a midsize city in central Tunisia, it was for more than four centuries North Africa’s leading link between East and West, a capital of power and the cradle of North African Arab culture that endures today.

It took the Muslim Arabs some 50 years to dominate central North Africa, which they called al-Maghrib al-Adna (the Nearest West) and the Romans called Ifriqiya. (Today this includes western Libya, Tunisia and eastern Algeria.) The Byzantines, with their stronghold at Carthage, ruled the coasts. Inland, Berber tribes controlled the oases. Arab general ‘Amr ibn al-‘As, who was sent to take control of Alexandria in 643 ce, 11 years after the death of Prophet Muhammad, afterward kept going west. With him was a nephew, a young officer named ‘Uqba ibn Nafi. According to Arabic sources, Ibn al-‘As sent his nephew on at least one raid south into central Libya. Though the Arab army was unable to hold onto any of the coastal ports and towns, Ibn Nafi’s experience proved valuable.
Twenty-seven years later, the caliphate—by then based in Damascus—decided to resume the campaign into North Africa. One of its goals was to establish a permanent base. Caliph Mu’awiya appointed Ibn Nafi to lead it.
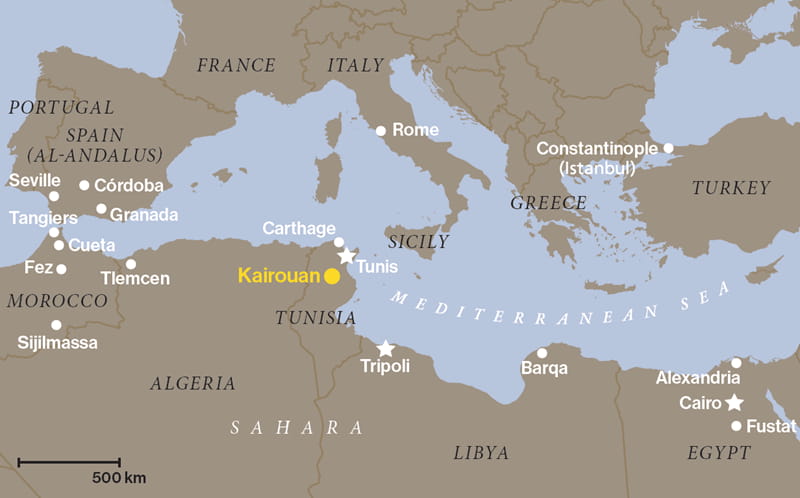
Ibn Nafi’s chosen site lay on an inland plain one day’s march from the sea—a safe distance from the Byzantine navy—and at an equally cautious remove from the highlands sheltering Berber tribes that variously allied with and fought the Arabs. Ibn Nafi named his site al-Qayrawaan, which Arabized the Persian word for caravan and today carries an English meaning close to “garrison camp.” Early Arab historians recount the site had been previously settled by both Romans and Byzantines, but it had fallen to ruin.
It proved an intelligent strategy. After constructing a large mosque and government house, it was from Kairouan that 12 years later Ibn Nafi and an Arab army set out farther west. Some sources claim he reached as far as the Moroccan coast.


Though he was ambushed and killed on his return to Kairouan by Berber rivals, his unexpected success helped leaders who followed to envision what became the further expansions of Muslim Arab power. Kairouan became the headquarters and the essential junction toward the rest of northern Africa and, after the Arab conquest of Iberia in 711, Europe. The reach of Islam and the cultural influences that followed exceeded those of any former civilization. In addition to Iberia, which became “al-Andalus” after its previous Vandal rulers, these extended along the entire southern Mediterranean coast, the Atlantic coast south into the Senegal River basin, and inland to the Sahara and the cities of the Niger River.
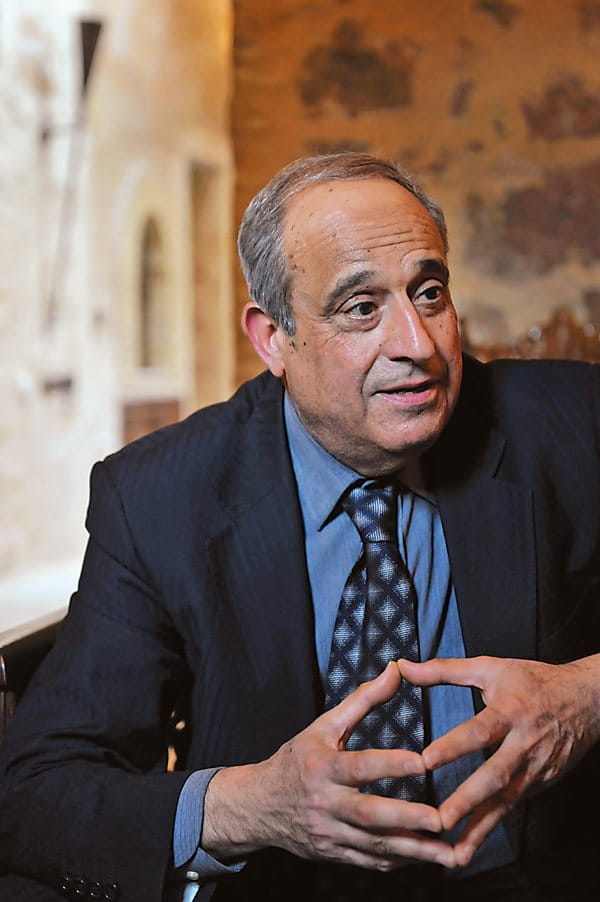
“Kairouan was born in a hostile environment, disputed and coveted by too many dynasties to name from the beginning,” explains Mourad Rammah, 66, a local historian and president of Kairouan’s Association to Safeguard the City. The association, he says, helped the city achieve its listing as a unesco World Heritage Site in 1988. Rammah descends from the Qays family, one of Kairouan’s oldest families that arrived with—or shortly after—Ibn Nafi himself. One of Rammah’s early-14th-century ancestors, Abu Abdallah al-Rammah al-Qays, was the city’s leading faqih, or jurist, as well as imam at the Great Mosque.
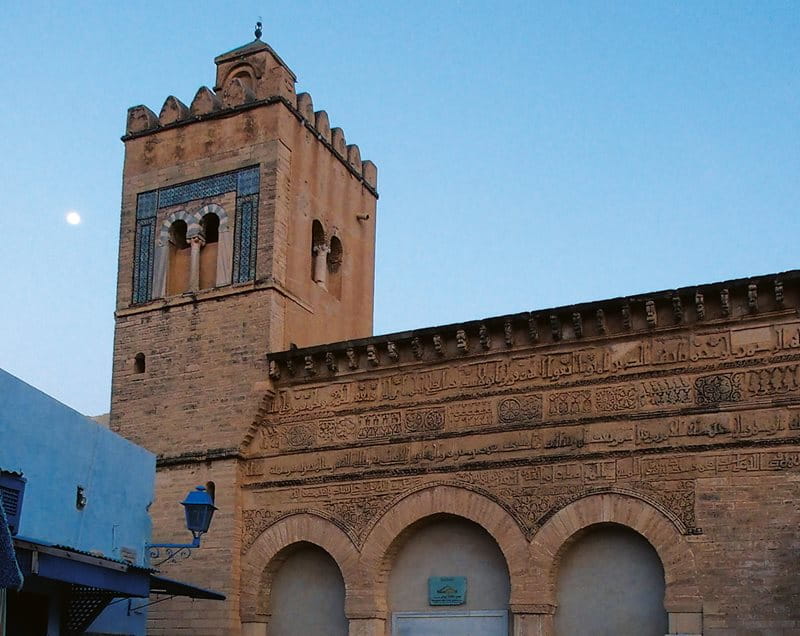
The governor’s house that Ibn Nafi built did not endure long, but the mosque, Rammah explains, was built on a such a grand scale that it could only have come from an early vision of a glorious, powerful city. Today it is the oldest mosque in North Africa. It has been rebuilt and renovated several times, most completely in the ninth century under the Aghlabids, whose rule marked the peak of Kairouan’s power.
Writing at the end of the 10th century, Arab geographer al-Muqaddasi described Kairouan as, “more inviting than Nishapur and bigger than Damas [Damascus], more prestigious than Isfahan.” Yet he was also a critic. “Its water is not good,” he wrote. “Its collection is done by storing rainwater in reservoirs.”
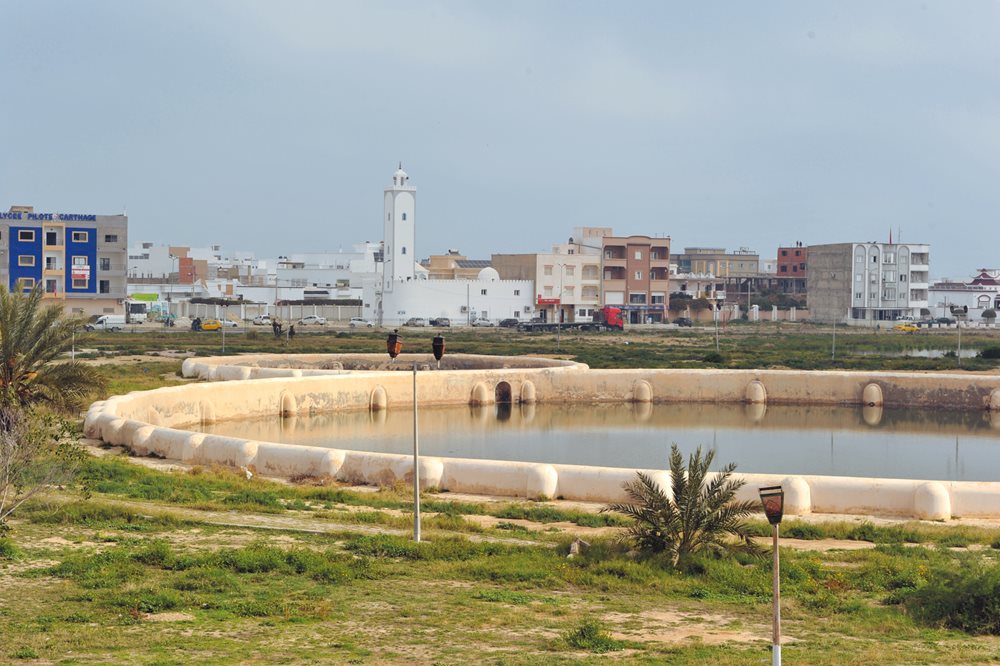

Al-Muqaddasi was referring to what was then the most advanced water supply system in any contemporary Islamic city: A century earlier, the Aghlabids had built 15 circular pools outside the city walls and filled them from rainwaters and the nearby wadi, or seasonal water channel. The largest pool was 128 meters in diameter and nearly five meters deep. It even had an octogonal tower in the middle where royals and high officials could relax. Today, the city conserves four of the cisterns as a public park and historic site.
Faouzi Mahfoudh is the general director of the National Heritage Institute in Tunisia’s capital, Tunis. The institute’s offices occupy a much-remodeled 11th-century palace that in the mid-19th century served as the town hall. Located in the heart of its madina, or old city, it is worth noting that on the patio to which Mahfoudh’s office opens, one can see the beauty of tiles belonging to different periods that integrate local and Italian influences.
Although Kairouan marks “the foundation of a country on the road of conquest,” Mahfoudh says that the city’s greatest importance comes from being Islamic North Africa’s “first point of culture” in religion, science, scholarship, law and architecture. It was in Kairouan, he explains, that the first university on the African continent was founded in the early 800s. Though it never carried a formal name, it influenced the founding of what is today the oldest continuously operating institution of higher learning in Africa, the University of al-Qarawiyyn in Fez, Morocco. It was started in 859 by a woman descended from ibn Nafi’s line, Fatima al-Fihri. To the east in Egypt, the Fatimid dynasty modeled Kairouan’s institution in 970 ce when founding the University of al-Azhar in Cairo. Also in Kairouan, says Mahfoudh, in the ninth century there was a multidisciplinary Bayt al-Hikma (House of Wisdom), along the lines of the one in Baghdad, that helped make the city a beacon of learning.


Spanish historian Luis del Mármol Carvajal, who wrote his accounts of the region in the 16th century, tells us that “in ancient times, people from all over Africa came to this university [in Kairouan], in the same way as the French go to Paris and the Spanish to Salamanca, and its elderly writers and doctors boasted that they have studied there.”
This rich exchange, Mahfoudh continues, “took place not only with the Arab Islamic world, but also with Europe.” Commerce helped expand relations with the African city, and propelled the expansion of knowledge and artistic influences. “The city became a laboratory of religions and cultures. It was a crossroads where elements taken from the west, such as Berbers, met Arabs from the east, and also Jews and Christians, too.”
Arab writer al-Ya’qubi, in the late ninth century, noted the presence in Kairouan of “Arabs from Quraysh, from Mudar, from Rabiya, from Kahtan and other tribes, too; Persians from Khurasan; finally, Berbers from Rum and still others.” Funerary inscriptions in the National Museum of Islamic Art in nearby Raqqada (see sidebar) show that Kairouan’s Christians kept their use of Latin throughout the city’s centuries of influence.
“Regarding the importance that the scientific field had in Kairouan, and only as some examples, for there are many,” Mahfoudh says, “we can mention two exceptional ones: the most celebrated [10th century] doctor and pharmacist, Ibn al-Jazzar, and Constantine, who was called Constantine the African, who introduced advances in medical science in Europe through the universities of Salerno and Montpellier.” Of Ibn al-Jazzar’s 43 known works, 10 have been preserved, most notably his general therapeutic manual Zad al-Mussafir wa-qut al-hadir, translated into Latin as Viaticum peregrinantis, which was used in Europe through the 16th century.


Constantine the African, Mahfoudh says, was a Christian who is generally believed to have studied in Kairouan before going on to teach medicine in Italy at Montecassino Abbey. There, he was also called “the Master of the East in the West,” as he devoted his energies to the translation of Arabic treatises, many of which he had carried there himself. His translations became fundamental almost a century and a half before Sicilians, Toledans and Venetians undertook systematic translation of medical and other scientific texts from the East.
Being such a renowned city, it is also not surprising that Kairouan became a famous destination for geographers and historians. (It has also been a destination for generations of pilgrims, with many claiming that Kairouan is the “fourth holy city of Islam.”) The travelers’ accounts, and the ways they portrayed the city in different times, illuminate the rise and eventual fall of the city’s urban and social fortunes.
Tenth-century geographer Ibn Hawqal is author of the Kitab fi surat al-ard (Book on the Configuration of the Earth). He was born in Mesopotamia, and his works included economic and political geography. Visiting Kairouan, he described it as
one the most important cities of the Maghreb, being above all others given its trade transactions, its wealth, the beauty of its buildings and markets. It is also the headquarters of the administrative power of all the Maghreb; here was where the tax collections took place, and the place for the government residence.
A century later, geographer al-Idrisi, from al-Andalus, described the city in words very much like Ibn Hawqal’s. However, he also wrote of its recent decline in his Kitab nuzhat al-mushtaq fi ikhtiraq al-afaq (Book of he who desires to journey through the climates):
This city is the mother of all metropolises and the capital of this setting. It was one of the most important cities in the Maghreb…. In its prosperous times, it had three hundred baths, the most part of them in private homes, and the rest open to the public. Now it has all became totally destroyed and depopulated.
Hassan al-Wazzan, the diplomat and traveler of the 16th century known in Europe as Leo Africanus and author of the General Description of Africa, noted Kairouan’s attempt to recover:
Nowadays, the city … starts to be repopulated, in a miserable way though. We can only see poor craftmen, most part of them goat and sheepskin tanners who sell their leather garments in Numidia, where European fabrics cannot be found. This craft provides them a hand-to-mouth existence.
What happened? Indeed, from the 10th century, cities such as Tunis, Marrakesh, Fez, Tlemecen and others had risen in power, weakening Kairouan’s role. Dynastic conflicts, too, took a toll. Kairouan’s population declined, although it maintained its importance as a pilgrimage center. In the late 10th century, the increasingly powerful Fatimid rulers moved their capital from Kairouan to their new city on the Nile, al-Qahirah (the Victorious)—Cairo. The economic and political blow was crippling. A plague followed some decades later. The coup de grâce came in 1045, when the nomadic tribes of the Bani Hilal began pillaging the city, and the region reverted to a largely pastoral economy.


Rammah says although Kairouan never again reached its former heights of achievement, its legacies shaped North Africa and Europe. “The intellectual basis of the western Islamic world was coined here,” he says. In daily life throughout North Africa today, this can be seen in the practice of Islamic law: Kairouan was the center for the development of the Malaki judicial thought, which today is one of the four main schools of law in Sunni Islam and the one predominant in North Africa.
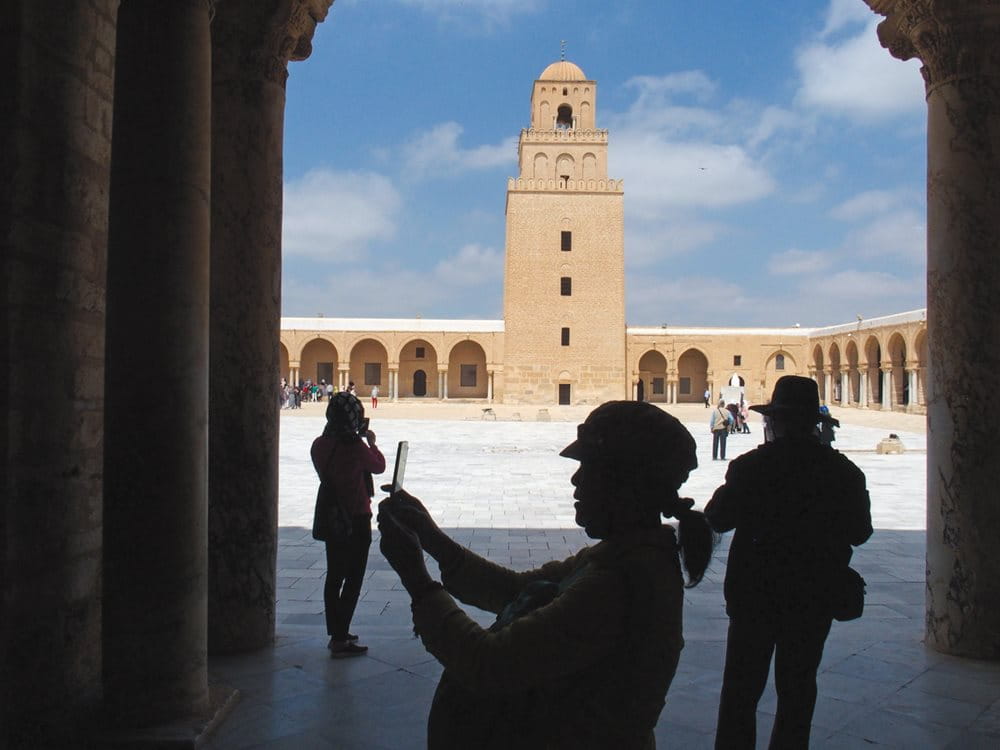
In architecture, the Great Mosque of Kairouan projected influence that can today be seen everywhere. Its simple, square minaret is now a solid and weighty contrast to the graceful, sky-piercing minarets built in later times to the east in later capitals. Kairouan’s minaret became a model that influenced designers of other minarets to the west and north. In Córdoba, Spain, the original minaret of the 11th-century mosque, around which the current cathedral tower was built, is much like that of Kairouan’s: three square cuboid layers topped by a domed cupola. From Tunisia west, nearly all minarets today are also square.
The Great Mosque’s 32-meter-high minaret remains the tallest building in Kairouan. Though now approached most often by car, the main streets still lead to it. As for travelers of old, it appears silhouetted on a hazy horizon, a hint of the reverent grandeur within its arcade-ringed plaza and column-forested prayer hall. It remains a kind of lighthouse of the desert, amid the scrublands and irrigated farms that, closer to town, give way to apartment blocks and shops, poles and wires, all the way to the old city walls. There, near the mosque, in between prayer times, tour buses lumber up to its doors and visitors disembark, spend an hour, take photos, and then return the space to silence until worshippers return for the next of the day’s prayers.

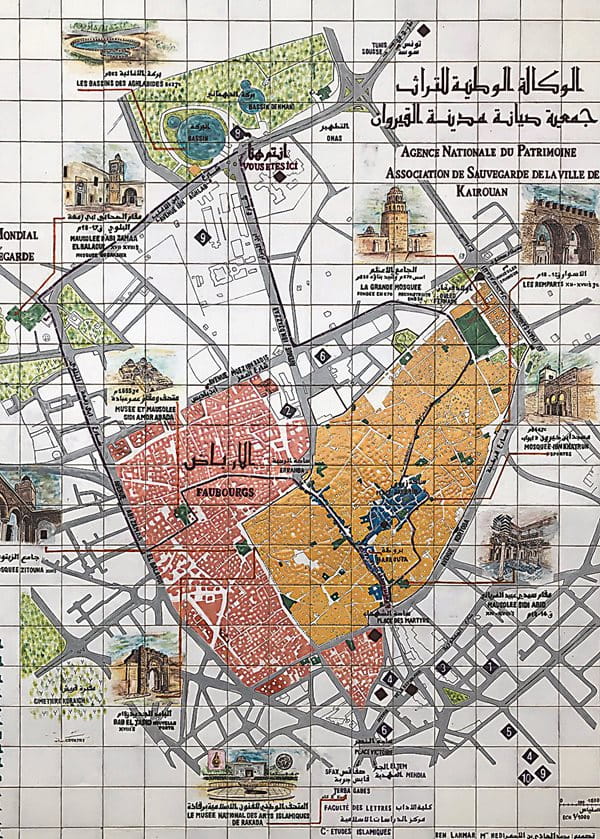
Outside the mosque hums the old madina, whose winding, pedestrian-only streets mix delapidation and restoration of more than 2,000 homes and small businesses for 17,500 residents, says Rammah. The urban pattern established here, he adds, separated craft guilds and set up rules for types of public and private spaces that, like the minaret, were imitated by other cities throughout Islamic North Africa.
In citing the city’s “universal value” as a World Heritage Site, unesco enumerated a total of 36 monuments in Kairouan, an “exceptional witness to the civilisation of the first centuries of Islam in North Africa.” Despite these accolades and the city’s long and many influences, Rammah laments that visitors remain relatively few compared to the many more who chase sun and sand at Tunisia’s coastal resorts.
About the Author

Ana M. Carreño Leyva
Ana M. Carreño Leyva lives in Granada, Spain, where she is a translator of modern languages and a freelance writer who specializes in the diverse cultural heritages of al-Andalus and the Mediterranean region.
Richard Doughty
Richard Doughty is editor of AramcoWorld. He holds a master’s degree in photojournalism from the University of Missouri.
You may also be interested in...

How Ancient Knowledge Shaped Modern Technology
History
Science & Nature
Part 3 of our series celebrating AramcoWorld’s 75th anniversary highlights the magazine’s emphasis on experts and institutions that push the boundaries of present-day knowledge while paying homage to historical figures and writings that paved their way.
Spotlight on Photography: Discover the Marshes of Iraq in a Visual Story by Wilfred Thesiger
Arts
History
“In the Marshes of Iraq” — November/December 1966
Voices That Shape Cross-Cultural Understanding
History
In its 75-year history, AramcoWorld has enlightened readers with stories about people throughout history and the modern world who have made an impact. Part 5 of our anniversary series examines the magazine’s positive portrayals of explorers, teachers, scientists and others to fulfill a mission of cultural bridge-building.


